LARRY
It's called a riffle shuffle.
AMITA
Larry has a history with Blackjack.
LIZ
That why you won't play with us
amateurs?
NIKKI
School us, Fleinhardt.
As the women check their cards, Larry continues--
LARRY
There are several categories of
shuffle-- Stripping, Hindu, Corgi,
Chemmy, Mongean, Faro--
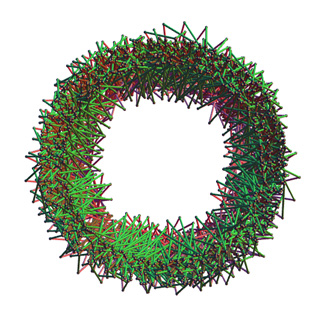
In a perfect
riffle shuffle, the deck is
split in half and cards are alternately interleaved from each half to form a new ordering. An
out-shuffle is one in which the bottom half of
the deck is used to start the interleaving, so that the bottom card always remains on the bottom. With an
in-shuffle, the top half is used to start the
ordering. For each type of shuffle, can you find how many shuffles are necessary to return the deck to its original
ordering?
As Larry speaks, Amita signals for three cards, Nikki for
two. Liz deals them out, takes one card for herself.
LARRY
Actually, Nikki makes a critical
point. Persi Diaconis at Stanford
proved a minimum of five shuffles
are required before a deck starts
to become random in the sense of
variation distance described in
Markov chain mixing time, but seven
shuffles are optimum.
NIKKI
That's all I'm saying.
AMITA
You think Don and Charlie got lost?
(throwing in more chips)
I'll bet another five.
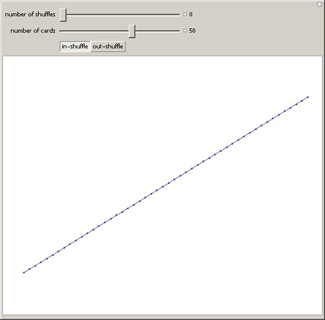
A decent first approximation of real market price activity is a
log-normal random walk. But with a fixed volatility
parameter, such models miss several stylized facts about real financial markets. Allowing the volatility to change
through time according to a simple
Markov
chain provides a much closer approximation to real markets. Here the Markov chain has just two possible states:
normal or elevated volatility. Either state tends to persist, with a small chance of transitioning to the opposite
state at each time step.
From a doorway, Liz and David peer into a slightly darkened
auditorium filled with students listening to a LECTURER just
finishing a slide presentation on the history of the
scientific method. (slides on Galileo, his experiments, his
mathematical equations.)
LECTURER
Though Galileo Galilei conducted
research by using experiments, he
argued his ideas in the form of
pure mathematics...
They spot JOSH LANDON sitting across the room, crumpled in a
seat, mesmerized by the slides. He looks more dissipated
than his photograph-- his hair is greasy and his clothes are
dirty and rumpled. (Another student sits next to him, CLOUD
JAMIESON (19) whom we will get to know soon.)
LECTURER (cont'd)
...a daring and creative evolution
of the scientific method. Galileo
gave us math as proof and predictor
of reality.
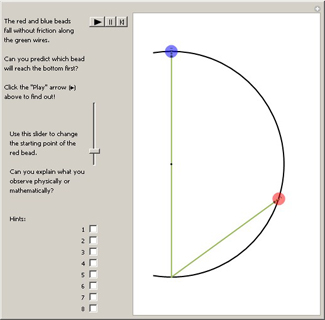
The blue bead falls straight down to the bottom of the circle along the vertical green wire. The red bead starts at a
lower point and slides without fraction diagonally, finishing at the same point as the blue bead. Can you predict which
bead will reach the bottom first?
Charlie and Amita pore over Josh Landon's writing.
CHARLIE
His papers are filled with
incoherent math and inductive
argument fallacies--
AMITA
In this one, he used reason to
prove that reason is not valuable.
CHARLIE
I think he has a larger intention--
(re: a paper)
Here's an ecological model of the
Prisoner's Dilemma proving altruism
in animals exceeds that of humans.
AMITA
What do you think he's getting at?
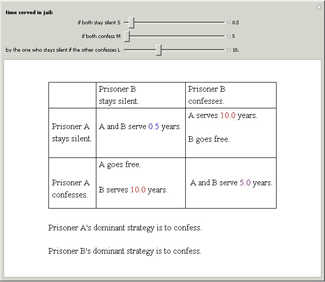
Two suspects, A and B, are taken into custody by the police. The police do not have sufficient evidence for a
conviction so they separate the prisoners and visit them individually to offer them the same deal. If one confesses and
will testify against the other while the other still stays silent, the one who testifies will go free while the other
will serve a very long time L in jail. However, if both confess, then both will spend a medium time M in jail.
Finally, if both stay silent they will serve a very short period of time S in jail.